Everything you need to know about life-threatening Placenta Previa
The complications of placenta previa are potentially harmful. For mothers, excessive bleeding could lead to death, while for babies, premature birth could lead to low birth weight and respiratory issues.
Do you have a low-lying placenta? Here is some important information about placenta previa and how it can affect your pregnancy.
If you’ve been keeping tabs on Pinoy celebrities, you may have heard of the term placenta preview when celebrity mom Divine Lee was rushed to the hospital due to her condition. Or maybe you know someone who had a delicate pregnancy due to having a low-lying placenta. But what causes a low-lying placenta and how does it affect one’s pregnancy?
We’ve gathered all the information you need to know about this condition.
Table of Contents
1. What is placenta previa?
Placenta previa, also known as low-lying placenta, is a condition in which the placenta lies low in the uterus. This results in a partial or complete block of the cervical opening (the part of the lower uterus that leads to the vagina).
The placenta is the organ that acts as a life support system to the developing fetus by passing oxygen and nutrition from mother to baby. It also eliminates waste from the baby’s blood. The placenta, where the baby’s umbilical cord develops, attaches itself to the uterine wall. If the placenta is low and blocks the cervical opening at the point of delivery, you would need to deliver via c-section.
There are three types of placenta previa.
- Complete previa where the cervical opening is completely covered.
- Partial previa where the placenta covers a portion of the cervix.
- Marginal previa where the placenta extends to the edge of the cervix.
Moreover, there’s also a posterior low-lying placenta, where the placenta is abnormally positioned and lies very low in the uterus, facing baby and anterior low-lying placenta, where the placenta is behind the baby.
According to the pregnancy website March of Dimes, placenta previa happens in 1 in 200 pregnancies.
While a low-lying placenta can be diagnosed as early as 12 weeks into the pregnancy, you really don’t have to work yourself up into a frenzy at this point. The condition is usually diagnosed as placenta previa only after 20 weeks.
The good news is that in almost 90% of cases, the placenta moves back up before the baby is due. As the uterus grows and stretches, the placenta moves higher in the uterus and away from the cervix.
In the event that it does not, the potential risk of severe maternal bleeding can occur. In some rare, unfortunate cases, a hysterectomy (surgery to remove the uterus) may be required to control the bleeding.
Watch this video for a more visual understanding of placenta previa.
2. Low-lying placenta symptoms
How do you know if you have placenta previa? While one-third of women who have a low-lying placenta don’t experience any symptoms, here are some signs you may also look out for:
- Bleeding. This is a warning sign not to be ignored. Once women enter their second trimester, it is extremely crucial to look out for vaginal bleeding as a sign of placenta previa. The bleeding is typically bright red and painless. It can range from light to heavy and is likely to occur when you cough, strain yourself or have sexual intercourse. While the bleeding does usually stop on its own, it is likely to return after several days or even weeks.
- Cramping. Though pain is uncommon, some women have experienced light to moderate cramping.
According to Dr. Elizabeth Ifurung Gonzales, an OB-Gynecologist from the Makati Medical Center, the position of a woman’s placenta during pregnancy is very important, since it can lead to bleeding in mothers.
“The only way to find out about the position of the placenta is through ultrasound. If it is on top, it may be hard to see baby. But if it is low-lying, it’s even more dangerous because it can cause the mother to experience bleeding,” she said in Filipino.
3. What causes a low-lying placenta?
The exact cause of placenta previa remains a mystery, but the following seem to be the largest contributing factors to the condition.
- Uterine Factors. Scarring of the lining tissues of the uterus. This is usually caused by previous surgery on the uterus for reasons such as removing fibroids (benign tumors of muscular and fibrous tissues that develop in the wall of the womb).
- Placental Factors. The position of the placenta is in direct relation to where the embryo plants itself in the uterus. Therefore, an embryo that plants itself low causes the placenta to also position itself low. Other placental factors include abnormally large placenta, such as in the case of multiple pregnancies.
Women are most susceptible to placenta previa when they:
- Have a history of abortion or multiple dilation and curettage (a procedure to remove tissue from inside the uterus)
- Had c-section (the risk increases with each subsequent c-section)
- Have endometrial scarring (bands of fibrous scar tissue that form within the uterus) from a previous episode of placenta previa
- Have had several children
- Are over the age of 35
- Do not have sufficient recovery and healing time between pregnancies
- Smoke
- Take cocaine
4. Placenta previa complications
The complications that can possibly arise out of complete placenta previa are not to be taken lightly.
Singapore specialist Dr. Iswaran Subrahmanyam cautions that placenta previa is “a very serious complication that can possibly cause maternal death”.
Similarly, America’s leading midwife Ina May Gaskin warns that complete placenta previa is “one of the most dangerous complications that can occur in any pregnancy”.
Complications women may experience are:
- Preterm labor. If heavy or uncontrollable bleeding occurs before the due date, the baby will have to be delivered immediately by c-section. Preterm birth may put the baby at risk of conditions like low birth weight and respiratory issues.
- Hysterectomy. Placenta previa can cause life-threatening hemorrhaging during and after delivery. This would call for a blood transfusion. In up to 10% of complete placenta previa cases, a hysterectomy may be required to control bleeding.
5. When to call the doctor
Bleeding would be the key indication to call your doctor. Even if the bleeding seems little or harmless, it is always best to err on the side of caution and get immediate medical attention.
From his 18 years of experience in Obstetrics & Gynecology, Dr. Iswaran says that he “cannot emphasize enough the importance of being alert, to ensure that your doctor is contactable at all times” and “never to delay seeking immediate medical help” in the case of bleeding.
6. Tests
Whether or not there is vaginal bleeding, your gynecologist will do an ultrasound during your 16 or 20-week check-up. This is done to determine the position of your placenta. In order to ensure that you are diagnosed accurately, it is likely that you will have an abdominal and transvaginal scan.
During the scan, extra precaution will be taken to ensure that the wand-like device inserted into your vagina will not disrupt your placenta. Your doctor will avoid performing routine vaginal examinations on you if placenta previa is suspected. This is to reduce any possible risk of heavy bleeding.
An ultrasound is used to diagnose and monitor placenta previa.
If you are diagnosed with or suspected to have placenta previa, your gynecologist will monitor you very closely for the rest of your pregnancy.
Additional ultrasounds will be performed to check on the position of your placenta, but pelvic and vaginal examinations will be avoided as much as possible. Your baby’s heartbeat will also have to be closely monitored.
7. Low lying placenta treatment
Unlike an infection or illness, placenta previa is not something that you can typically cure by administering medication. You might be given medication to prevent preterm labor and, ideally, to help your pregnancy to progress to the 36th week.
If it is likely that you have to deliver earlier than your due date, you may be asked to take steroid injections to strengthen your baby’s lungs. You will also be asked to closely follow these preventive measures:
- Avoid any kind of strenuous exercise or activities
- No lifting of heavy objects
- Avoid sexual intercourse
- Bed rest
- Avoid pelvic examinations
- Hospital bed rest (for heavy bleeding)
- Blood transfusion (if too much blood has been lost)
- No douching (washing or cleaning out the vagina with water or other mixtures)
If the bleeding persists or your baby starts showing any signs of distress, the only solution would be an emergency c-section. This is crucial for the safety of you and your child.
If the bleeding continues after your baby is born, and if your life is at risk, you may require a hysterectomy.
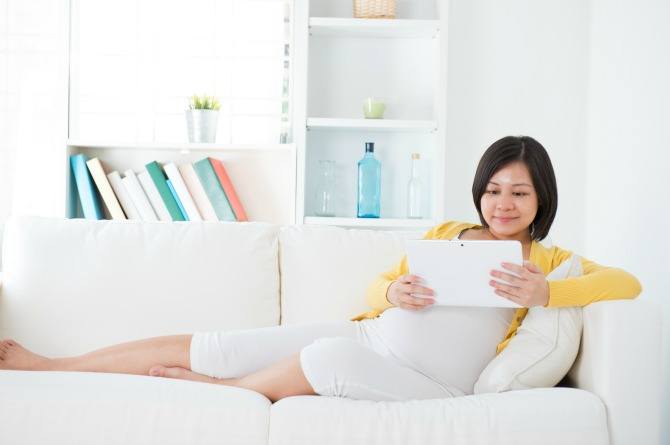

If you’re diagnosed with placenta previa, the most important thing to do is to take it easy to avoid complications.
8. Lifestyle and Home Remedies
The most important thing to do if diagnosed with placenta previa is to take it easy.
If being idle is not your cup of tea, you may want to think again. When your precious bundle of joy arrives, idle time will be a thing of the past.
For moms with toddlers or small children, you might want to look into arrangements for an extra hand. You could consider temporarily staying with your parents or hiring a helper.
It is crucial that you do not exert or strain yourself in any way. And that includes not carrying your older children.
Low lying placenta travel restrictions
While pregnant women are allowed to travel by air up to one month before their due date, complicated pregnancies including placenta previa are not allowed to fly as it may put their pregnancy at risk. So save the air travel for another time.
Low lying placenta sleeping position
Is there are recommended position for pregnant women with placenta previa?
Depending on the severity of the condition, some women are advised to go on bed rest especially during the second trimester of pregnancy. But while there is no specific sleeping position recommended for women with low-lying placenta, it’s just best to sleep in the position you’re most comfortable in. However, in the latter half of the pregnancy, it is best to sleep on the side.
So really, slow down, grab a cup of tea, and rest in bed with a good book for company. Reading will help to ease you off some of the anxiety and stress that you might be going through.
9. Prevention
While there is no fail proof method of preventing placenta previa, knowing and understanding the risks may help to lower the odds of it occurring.
For example, smoking and the consumption of cocaine greatly increase the chances of placenta previa. If you have any such addiction during, or when planning a pregnancy, seek help immediately.
You may also wish to consider factors such as your age and how many children you’ve already had. Especially if you have undergone any kind of surgery on your uterus, it would be a good idea to speak to a gynecologist before trying to conceive.
Forward planning is ideal in any situation.
While it is definitely not a condition that you would take lightly, do not let it take too much of a toll on you. Most importantly, take the necessary precautions, take the best possible care of yourself, go for frequent check ups and try your best to stay positive!
Additional information from Camille Eusebio
Republished with permission from theAsianparent Singapore.
Here at theAsianparent Philippines, it’s important for us to give information that is correct, significant, and timely. But this doesn’t serve as an alternative for medical advise or medical treatment. TheAsianparent Philippines is not responsible to those that would choose to drink medicines based on information from our website. If you have any doubts, we recommend to consult your doctor for clearer information.